Miyagi Prefecture
| Miyagi Prefecture | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Capital | Sendai | ||||||||
| Region | Tōhoku | ||||||||
| Island | Honshū | ||||||||
| Governor | Yoshihiro Murai | ||||||||
| Area (rank) | 7,285.16 km² (17th) | ||||||||
| - % water | 0.3% | ||||||||
| Population (October 1, 2002) | |||||||||
| - Population | 2,370,280 (15th) | ||||||||
| - Density | 325 /km² | ||||||||
| Districts | 10 | ||||||||
| Municipalities | 36 | ||||||||
| ISO 3166-2 | JP-04 | ||||||||
| Website | www.pref.miyagi.jp/ english/ |
||||||||
| Prefectural symbols | |||||||||
| - Flower | Miyagi bush clover (Lespedeza thunbergii) | ||||||||
| - Tree | Japanese zelkova (Zelkova serrata) | ||||||||
| - Bird | Wild goose | ||||||||
| - Fish | |||||||||
 Symbol of Miyagi Prefecture |
|||||||||
| Template ■ Discussion ■ WikiProject Japan | |||||||||
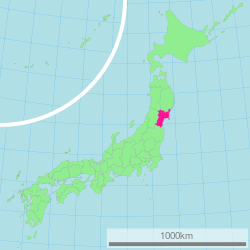
Miyagi Prefecture (宮城県 Miyagi-ken) is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku Region on Honshū island. The capital is Sendai.
Contents |
History
Miyagi Prefecture was formerly part of the province of Mutsu. Mutsu Province, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Ainu and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient capital was in modern Miyagi Prefecture.
In the 3rd month of 2nd year of the Wadō era (709), there was an uprising against governmental authority in Mutsu Province and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were promptly dispatched to subdue the revolt.[1]
In Wadō 5 (712), the land of Mutsu Province was administratively separated from Dewa Province. Empress Gemmei's Daijō-kan continued to organize other cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period, as in the following year when Mimasaka Province was divided from Bizen Province; Hyūga Province was sundered from Osumi Province; and Tamba Province was severed from Tango Province.[1]
During the Sengoku period various clans ruled different parts of the province. The Uesugi clan had a castle town at Wakamatsu in the south, the Nambu clan at Morioka in the north, and Date Masamune, a close ally of the Tokugawa, established Sendai, which is now the largest town of the Tōhoku region.
In the Meiji period, four new provinces were created from parts of Mutsu: Rikuchū, Rikuzen, Iwaki, and Iwashiro.
The area that is now Aomori Prefecture continued to be part of Mutsu until the Abolition of the han system and the nation-wide conversion to the prefectural structure of modern Japan.
Date Masamune built a castle at Sendai as his seat to rule Mutsu. In 1871, Sendai Prefecture was formed. It was renamed Miyagi prefecture the following year.
Geography
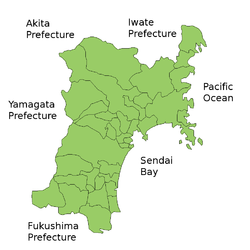
Miyagi Prefecture is located in the central part of Tōhoku, facing the Pacific Ocean, and contains Tōhoku's largest city, Sendai. There are high mountains on the west and along the northeast coast, but the central plain around Sendai is fairly large.
Matsushima is known as one of the three most scenic views of Japan, with a bay full of 260 small islands covered in pine groves.
Oshika Peninsula projects from the northern coastline of the prefecture.
Cities
Thirteen cities are located in Miyagi Prefecture:
|
|
Towns and villages
These are the towns and villages in each district:
|
|
|
‡ Scheduled to be dissolved following mergers.
Mergers
Future mergers
- Both towns within Watari District are planning to merge and create a new city under the name of Watari. Watari District will dissolve if the city is created[2]
Economy
Although Miyagi has a good deal of fishing and agriculture, producing a great deal of rice and livestock, it is dominated by the manufacturing industries around Sendai, particularly electronics, appliances, and food processing.
Demographics
Culture
Sports
The sports teams listed below are based in Miyagi Prefecture.
- Football (soccer)
- Vegalta Sendai (Yurtec Stadium, Sendai)
- Sony Sendai F.C. (Tagajō)
- Baseball
- Tohoku Rakuten Golden Eagles (Miyagi Baseball Stadium, Sendai)
- Basketball
- Sendai 89ERS (Sendai Gymnasium, Sendai)
Visitor attractions
Sendai was the castle town of the daimyo Date Masamune. The remains of Sendai Castle stand on a hill above the city.
Miyagi Prefecture boasts one of Japan's three greatest sights. Matsushima, the pine-clad islands, dot the waters off the coast of the prefecture.
The following are also noted as attractions:
|
|
Prefectural symbols
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). Annales des empereurs du japon, p. 64.
- ↑ "カーシェアリングがわかった!". http://www.w-y-gap.jp/. Retrieved 2008-06-14.
External links
- Official Miyagi Prefecture homepage last accessed on March 25, 2007
- Official information of each merger in Miyagi Prefecture last accessed on March 25, 2007
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||